Gaming PC purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What you need to know
- Gaming PCs are particularly powerful computers designed for high-end gaming.
- With a gaming PC, the players themselves determine how powerful the hardware should be.
- Should the technology no longer be up-to-date, the hardware can be updated according to the user’s preferences; consoles don’t have this option.
- For smooth gameplay, the CPU, graphics card, and RAM in particular should have above-average performance and adequate cooling.
- In addition to high-end gaming, such a gaming PC can also be used for office work and demanding tasks such as photo editing, video editing, and 3D modelling.
Benefits of a gaming PC
A modern gaming computer is the holy grail for all those who love video games. A wide selection of game titles ensures long-lasting fun. Powerful graphics chips supply the matching gaming monitor with breathtaking Full HD or even 4K images. The landscapes in many game worlds are so beautiful that users won’t want to stop gaming. If individual components become outdated and no longer fully meet the requirements of modern games, the biggest advantage of a gaming PC is that one can replace individual hardware parts with newer ones.
Initially, it is advisable — especially for those who aren’t technophiles — to buy a pre-assembled gaming computer that meets your wishes and requirements and is ready for immediate use. When it reaches its limits after a certain period of time, gamers have several options to enable a smooth gaming experience. This typically occurs two to five years after the initial purchase.
Gamers can then commission a specialist to replace individual hardware components or buy components and insert them into the existing case themselves. The option of upgrading outdated hardware to modern technology is a great advantage that PC users have over console gamers.
Whether by a specialist or on their own: either way, users can easily upgrade the processor, RAM, or the graphics card to the latest state of the art model. In this way, the gaming computer achieves even faster loading times and supports higher resolutions. Users can choose between different hardware manufacturers who offer products with a wide range of performance and an equally wide price range. Thus, unlike with a gaming console, gamers are not limited to a particular hardware manufacturer.
However, it is important that the hardware matches, both in terms of interfaces and performance. If the interfaces are different and incompatible, it won’t be possible to use them at all. If one component outperforms the others by far, it will be slowed down by the least powerful one. Therefore, the individual components should belong to approximately the same performance class and generation. Potential buyers who are not confident enough to do this themselves are better off choosing a pre-configured system or asking someone else for assistance.
All in all, a computer made for gaming will result in shorter loading times and higher playable resolutions. Switching from Full HD to 4K means a quadrupling of the pixels displayed, and thus a disproportionately higher level of detail, which has a positive effect on the overall experience. For such visual results, however, in addition to the computer, a corresponding monitor or TV is also necessary that enables such resolutions.
Flexibility
Although some consoles can now keep up in terms of resolution, what makes a gaming computer is the freedom of the user: in addition to the choice of components, they can also freely choose from a range of peripherals such as keyboards, mice, gamepads, steering wheels, VR goggles, and webcams from different manufacturers. With the console, they are often locked into a given control device. The same applies to communication tools such as chat programmes: while the computer user is free to choose, the console manufacturers specify which programmes can be used. Usually, the choice is limited by the device’s own app store.
Another argument in favor of gaming computers: for many games, so-called mods, i.e. game modifications, which are often free and created by hobby game developers, are available for certain computer games. They help to increase the popularity, quality, and longevity of a game. For consoles, on the other hand, only manufacturer mods are available, usually for a fee. These are also called downloadable content (DLC).
Exclusive game titles on the PC
Another important reason for buying a gaming computer is the fact that some titles are only available for Windows PCs. Console gamers and users of other operating systems are, therefore, not able to play such games. A gaming computer usually runs the latest version of Windows and thus meets that requirement. Below, we list a selection of popular games that only reached PC users.
- Anno 1800 (2019)
- Age of Empires: Definitive Edition (2018)
- Quake Champions (2018)
- World of Warcraft (2005)
- League of Legends (2009)
The most important components
Computers that are mainly used for gaming need a number of powerful components. In the following, we present the individual parts, go into their function, and give a brief overview of what is available on the market.
The mainboard: control center for all data streams
The mainboard, also called motherboard, is the foundation on which the gaming PC is built. Power is distributed from the power supply unit to the individual components via various interfaces. It also controls the exchange of data between components such as a hard disk drive, graphics card, CPU, and RAM. When choosing the right mainboard, you must pay attention to several factors.
The mainboard must have a suitable socket for the desired processor. This already limits the choice slightly. In addition, there are various sizes, which in turn must fit into a selected housing. It is advisable to choose a large mainboard model, as long as it fits in your tower. Large mainboards naturally offer more space for interfaces than smaller models. Moreover, the individual interfaces usually have a greater distance from each other. This can be an advantage if you want to use large components such as high-end graphics cards. If, on the other hand, you opt for a smaller mainboard, you could face the problem that your components interfere with each other and do not find enough space on the board. The choice of mainboard determines the component interfaces – first choose a mainboard and then the matching components.
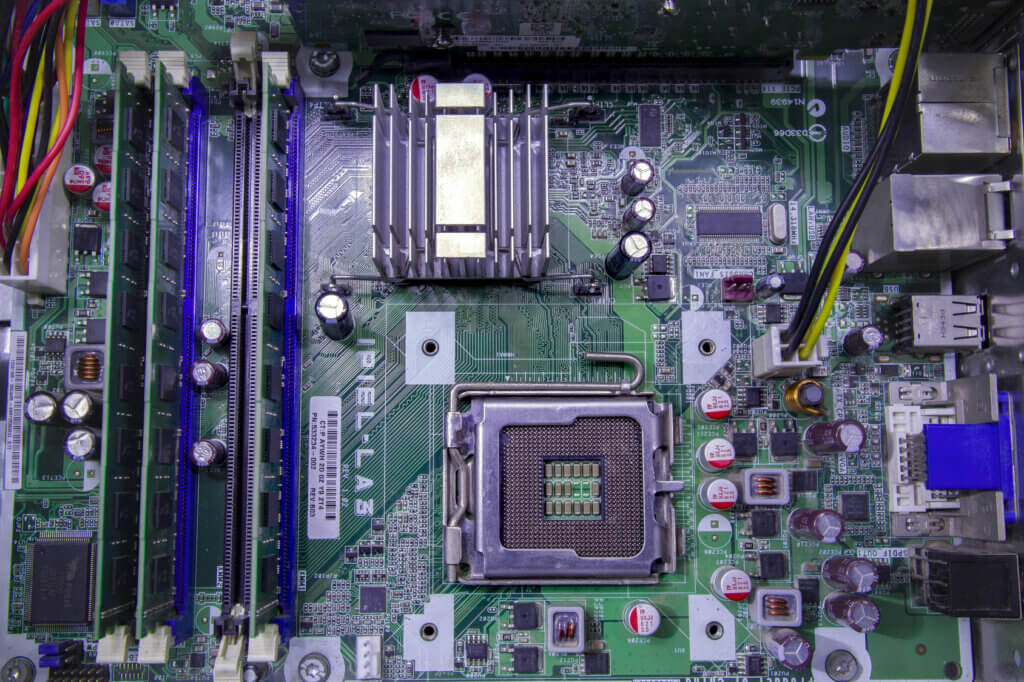
The processor: the control center for all computing operations
The processor, also known as the CPU (Central Processing Unit), forms the control center of a computer. It processes the data sent by the other hardware components.
Single- vs. multi-core processor
Traditionally, one processor core was installed in processors. However, technology has advanced to the point where several processor cores are installed in one CPU. That is called a multi-core processor. In accordance, dual-core processors house two cores, quad-core systems four, and octa-core processors eight. Visually, such a multi-core processor cannot be distinguished from a single-core version. During computer operation, the individual cores are treated as multiple computing units. The result is that users can perform several computing operations at the same time. In the high-end gaming sector, single-core processors no longer have a place.
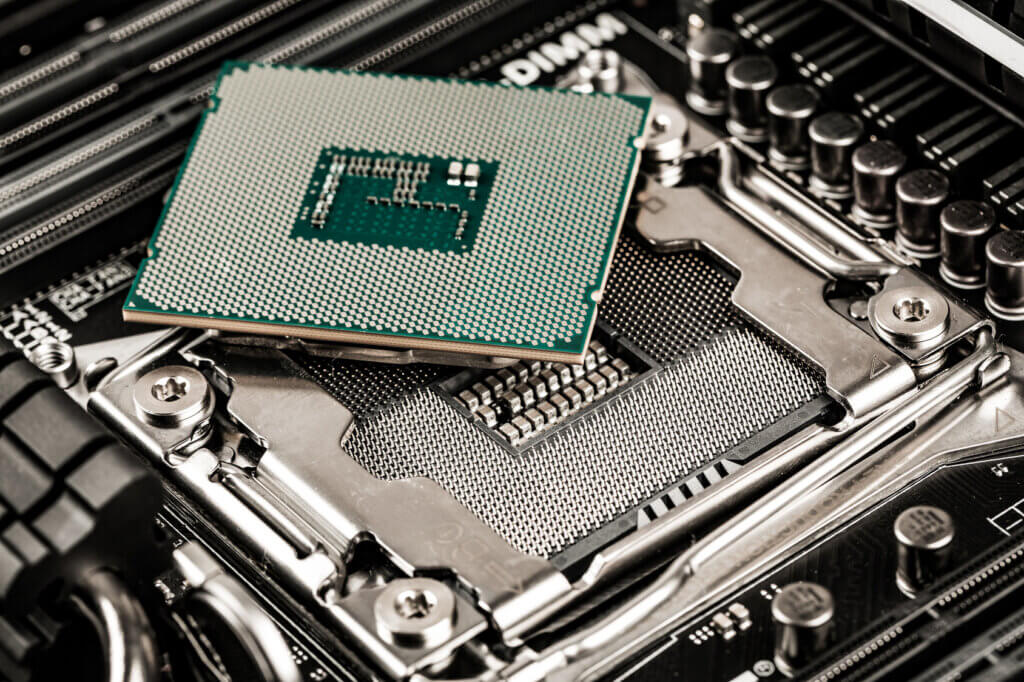
A multi-core processor therefore usually means a significant increase in performance; the more cores a processor has, the more powerful it usually is (the performance of each individual core is also relevant). How big the performance increase is, however, also depends on whether software supported by this hardware is able to address several of the cores simultaneously. Another important factor is whether the user has a 32- or 64-bit operating system.
32- and 64-bit architecture in operating systems
Processor architecture refers to the structure of a processor core. In earlier Windows operating systems, such as Windows XP, the 32-bit architecture was primarily used. This design is associated with certain limitations. For example, the operating system architecture can only process four gigabytes of RAM. With 64-bit processors, which found their way into gaming PCs from Windows Vista onwards, the main advantage is the increased address range, i.e. the size of the RAM that can theoretically be addressed: with 64-bit systems, it amounts to 16 exbibytes of RAM, which is far more than the memory sizes available for high-end gaming. Gamers benefit from this increased range because larger amounts of data can be processed simultaneously by several CPU cores. This shortens loading times and prevents in-game glitches when generating the game world.
There are two main chip manufacturers that compete on the market: Intel and AMD. In the following, we present the different product ranges of the two suppliers. Beforehand, however, it can already be stated that, for gaming, the CPU should be at least a quad-core processor with a clock speed of three or better four gigahertz.
Intel processors
The US chip manufacturer Intel markets its current processors as the Intel Core i series. The manufacturer divides its processor range into four performance classes: i3, i5, i7, and i9. The higher the class number, the more power the chip delivers. This is also reflected in the purchase price. However, the classification into a category alone does not help.
An i5 processor with a high model number may be more powerful than an i7 processor with a low model number. Category numbers 3 to 9 are followed by a model designation consisting of four numbers. In the example of the i7-4770, it means that it is a powerful fourth-generation i7 processor. The remaining three digits, 770, stand for the model designation. The higher the numbers, read successively from left to right, the more powerful the processor.
AMD processors
AMD computer processors have caught up in recent years and are once again competitive. The chip series for gaming computers that is comparable to the Intel Core processors is called Ryzen. Similarly to Intel, the manufacturer designates the CPUs with the category names Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, and Ryzen 7. The competitor model to the Intel Core i9 in the high price range is called Threadripper by AMD. Here, too, the category numbering is followed by a four-digit model designation, such as AMD Ryzen 7 2700. The 2 also stands for the second generation and the 700 for the model designation. By naming its processors this way, AMD deliberately makes comparing its processors to the competition from Intel easier.
In addition, AMD offers low-priced processors for the entry-level and lower mid-range with its low-cost FX series. These are suitable for users who play older games without wanting to use the maximum graphics settings. These economical alternatives are not suitable for newer adventure games or shooters with 3D graphics and a full HD or 4K resolution. In addition, the architectures used are usually outdated and it becomes increasingly difficult to find suitable hardware such as mainboards or RAM modules over time.
Which processor manufacturer is ‘better’?
This question is not so easy to answer. With earlier models from the manufacturer AMD, a direct comparison with Intel was difficult for consumers, as different clock rates were used. Ever since the Ryzen model series, this is no longer the case. In addition, AMD has caught up strongly. Which manufacturer supplies the better CPU is often a question of preference. Both suppliers have a loyal following that swears by their respective products. It can generally be said that a different processor is recommended for each application and each user. So-called benchmark tests simulate a wide variety of accesses, such as office tasks, video editing, and gaming. The performance figures determined for the various categories make it possible to compare the individual models. In this way, every user can find the right product. For the average gamer, processors of the 3-series are out of the question. They should therefore opt for a current 5– or 7-series model from Intel or AMD. The processors of the 9-series (Intel) or AMD’s Threadripper processor are rather expensive. They are therefore primarily suitable for enthusiasts and pros who do not want to compromise on performance. What is more, the other components of such a high-performance system must also be correspondingly high-performance in order to let the fast processor fully come into its own.
Graphics card: the heart of graphics splendor
Next to the processor, the graphics processing unit (GPU) plays the most important role in calculating data in games. If the graphics card, the heart of graphics performance in the network of PC components, is not powerful enough, it can form a bottleneck in terms of performance. The main memory installed in the graphics unit is also of crucial importance. In this segment, users have a choice between two different suppliers. Nvidia and AMD.
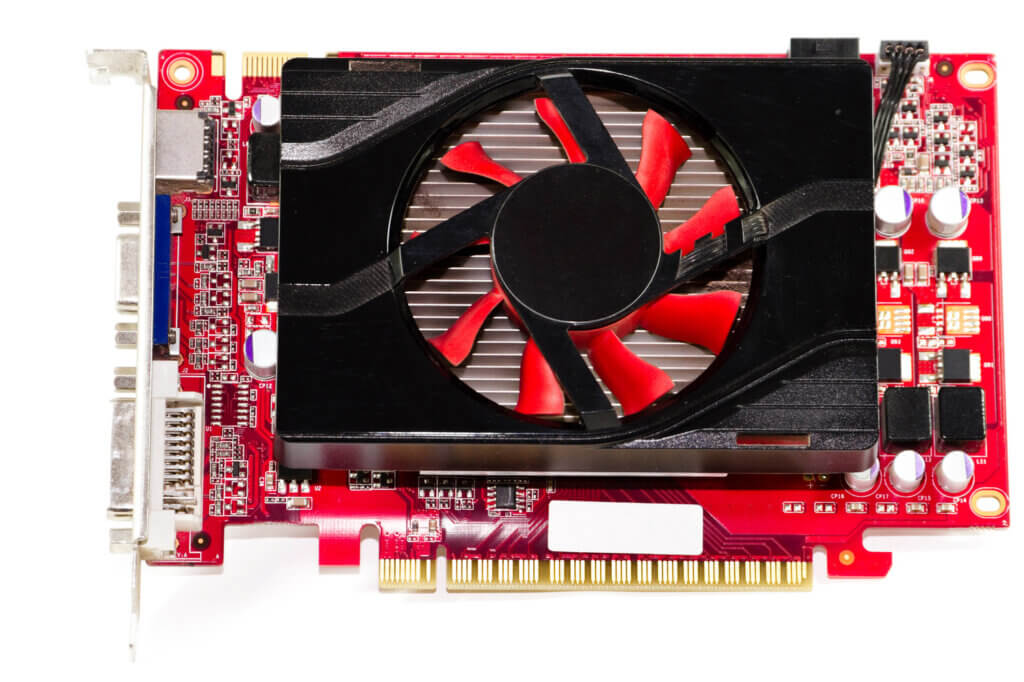

Nvidia GeForce series
The GeForce graphics cards from the manufacturer Nvidia are an established brand. Here, interested parties will find powerful mid-range to high-end graphics modules. Especially in the high-end sector, the Nvidia models are in the lead; AMD currently cannot match this performance. On the other hand, the powerful GPUs are comparatively expensive. They can quickly cost over $1,000 and more. Of course, there are still cards available for the broad mass of users that cost around $300 to $350.
AMD Radeon series
In 2006, the US chip developer AMD took over the Canadian graphics and chipset specialist ATI, which had successfully established the Radeon graphics card series on the market. Especially in the entry-level and middle class, the US competitor of Nvidia offers an unrivalled price-performance ratio. Potential buyers who don’t want to play at the highest resolutions and for whom a moderate setting is sufficient get good performance at a low price. The manufacturer has caught up strongly in recent years and could also become fully competitive in the high-performance sector in the near future.
Radom-access memory: fast access times
The random-access memory (RAM) serves as the computer’s direct access memory. It loads the required data for all the programmes that are in use at the time. This shortens the access time considerably compared to reading out an entire HDD. In addition, it is a volatile memory. This means that it empties completely when the device is switched off. Since the processor directly accesses this memory unit, its size and transmission speed directly influence the performance of the entire gaming computer. The access speed provides information about the time it takes for data to be accessed.
The memory speed, on the other hand, specified in megahertz (MHz), determines the amount of data that can be read per second. In addition to this information, the memory size of the individual RAM bars is also important, which is usually between one and eight gigabytes. It is important because many applications occupy large amounts of the random-access memory during operation; having many tabs open simultaneaously can cause processes to come to a standstill even if the 8 gigabytes are otherwise adequate.
Prospective buyers must always pay attention to which type of slot modules fit the mainboard. There are now five different DDR SDRAM standards (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory).
Buyers must therefore refer to the description of the mainboard to find out which main memory components are compatible. Mixing DDR RAM versions, for example between DDR2 and DDR4, is not possible due to different voltages and partly different designs. A higher version number after the “DDR” describes a newer, faster model:
- DDR-SDRAM, 3.2 GByte/s
- DDR2-SDRAM, 6.4 GByte/s
- DDR3 SDRAM, 12.8 GByte/s
- DDR4 SDRAM, 17.0 GByte/s
- DDR5 SDRAM, 19.2 GByte/s
Mixing components of the same DDR RAM version from different manufacturers and memory sizes should be done with caution: it is possible that the slowest component also throttles down the faster components to its speed. In this case, not all the memory space would be available.
Hard disk drive: data storage
The main memory stores data permanently. A general distinction is made between the classic HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and the more modern flash memory called SSD (Solid State Drive). However, hybrid storage as a combination of both types is also available.
Magnetic hard disk drive: proven and affordable technology
The hard disk drive (HDD) is a magnetic storage medium in which data is written to the surface of rotating discs. This type of storage medium has been used in private computers since the 1980s. On it, users install the operating system as well as other data such as MS Office documents, photos, or videos. Previously with little storage space and comparatively expensive, hard disks with large storage capacities of one terabyte or more have become increasingly affordable over time.
Therefore, these magnetic hard disks are still used in computers and laptops today. However, there is now a faster option, namely SSDs. In addition, magnetic hard disks are susceptible to physical damage due to wear and tear or falls. The reason: this type of hard drive has moving parts such as magnetic disks, a write and read head with a motor, as well as other physical components that can be damaged. In the event of damage caused by a fall or motor failure, the data can only be reconstructed by specialists at great expense. In the worst case, all contents stored on the data medium are lost. It is therefore generally recommended — regardless of the type of hard disk used — to make regular data backups. You can either use an external hard drive, a USB stick, or a cloud storage service for this purpose.
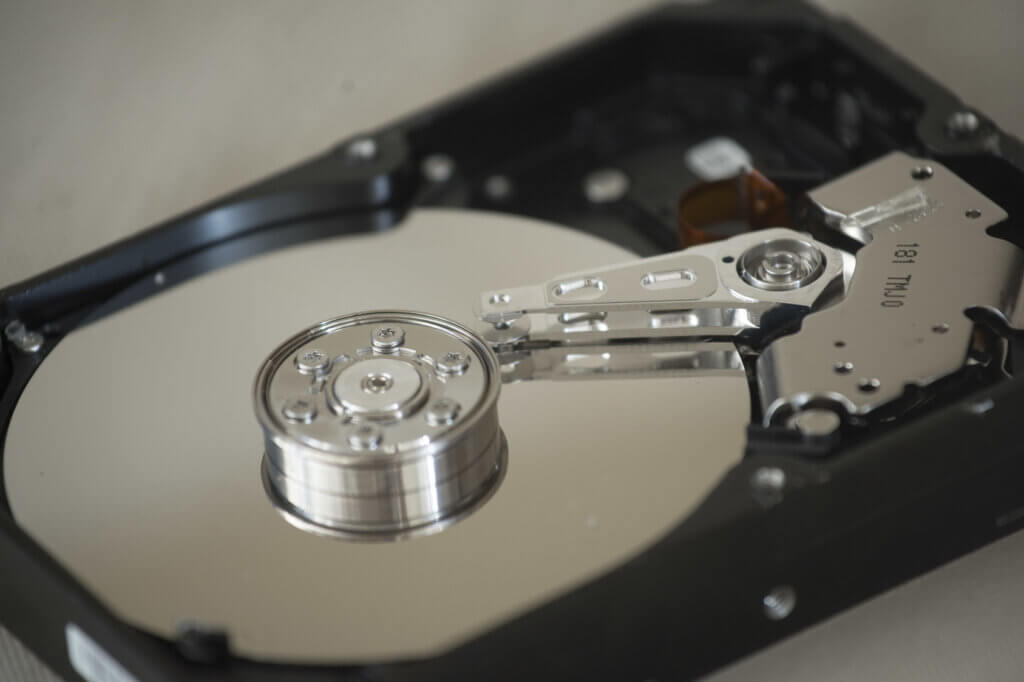

Advantages
- Large storage capacities at comparatively low prices
- Many read and write operations possible
Disadvantages
- Mechanical components susceptible to physical damage
- High space requirement in the PC housing
- Comparatively low read and write speed
SSD flash memory: compact and fast
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are compact flash drives. Their technology resembles a USB stick. In contrast to the classic magnetic hard disks, these flash memories no longer work with a read and write head, but access all memory areas (individual cells) at the same speed. These individual areas can only be rewritten a limited number of times. Their maximum number of write operations is therefore lower than that of classic hard disks. Each time a file is written to its memory, the life of the SSD decreases. However, it has an access algorithm that protects against rapid wear. An SSD basically distributes new data evenly across its individual memory cells. All cells are used approximately the same number of times. Thus, a failure of individual, heavily used cells is unlikely.

The great advantage of SSDs is that no read head has to “search” for the data as with a magnetic hard disk. Instead, SSD memories directly address the memory cell and the file stored in it. This leads to a speed advantage. Due to their comparatively small size and lower susceptibility to physical damage such as shocks and falls, SSDs are increasingly being installed in mobile devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones in order to make the devices smaller and more robust.
Advantages
- Immobile components are less susceptible to shocks
- Comparatively high read and write speed
- Compact design
Disadvantages
- Fewer read and write operations possible than with a classic hard drive
- Large storage capacities still comparatively expensive
Hybrid storage: the advantages of both technologies combined
An SSHD (Solid State Hybrid Drive) combines a classic magnetic hard disk and a modern SSD memory. The storage space on the SSD part is comparatively small, while the space on the magnetic storage medium is large. The trick is that users install important system files such as the operating system or frequently used programmes on the SSD part. This significantly speeds up the system: processes such as booting up and shutting down, but also system services and games are executed very quickly. Other data, such as infrequently used programmes and the potentially large archive of holiday photos and application documents, are stored on the HDD storage part, where there is significantly more space. System processes are processed particularly quickly in this way, games start promptly and loading times are reduced to an easily tolerable level. Access times for data like personal photos are less important, so they are stored on the slower part of the hard disk. This design ensures a good price-performance ratio. However, if a component of the composite is defective, users have to replace the entire module.
Advantages
- Good price-performance ratio
- Fast system
- Plenty of space for files like photos and videos
Disadvantages
- Replacement of the entire module necessary if one part is defective
Casing: find space for all components
The computer casing is particularly important to many gamers, as the first impression often lingers. Many users consider the shape and color as well as special lighting elements to be important. Thus, some casings have a viewing window made of Plexiglas on one side and provide an exciting insight into the PC’s inner workings. Noise-insulating materials that keep the computer’s operating noise in check are also popular. Above all, however, it is important that the casing is the right size to accommodate the mainboard and all the components installed. There must also be threads to ensure that the motherboard is securely fastened. In addition, there must be sufficient space for cooling and ventilation. Some casings also have their own pre-mounted casing fans.
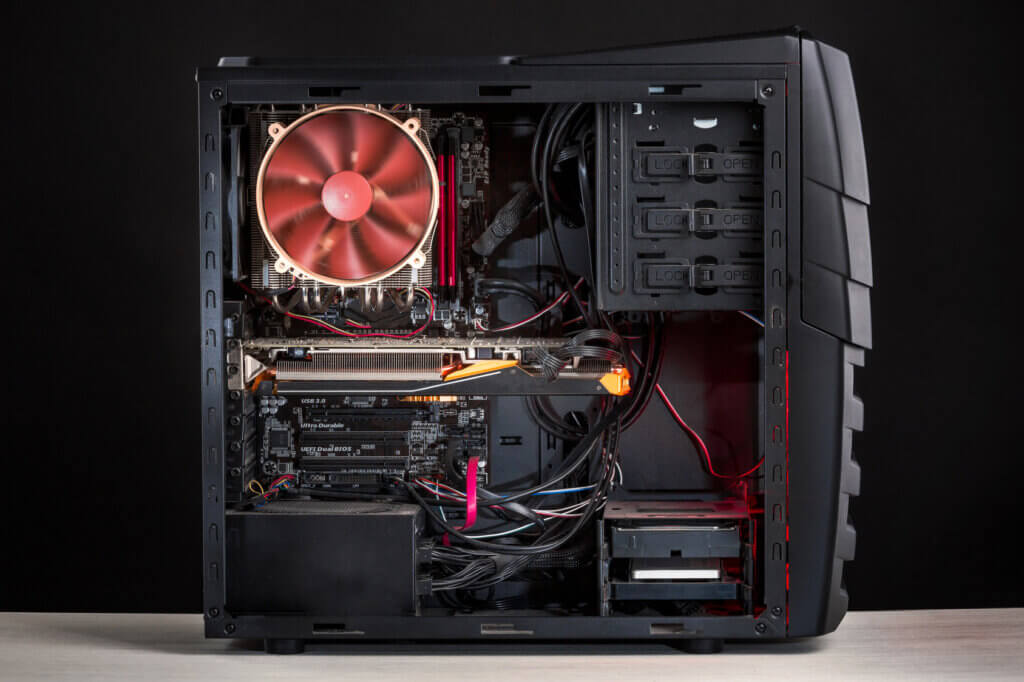

Fan and cooling system: preventing overheating
Certain components of gaming computers, especially the processor and the graphics card, emit a lot of heat. To prevent the components from getting too hot, an effective cooling system is necessary. This can be an air or water cooling system. In the case of an air-cooling system fans are used, which discharge heated air from the enclosure or supply cool ambient air at adapted speeds, in order to cool down the components as they heat up. With powerful components and demanding software such as modern games, fans have to rotate very quickly in order to guarantee sufficient cooling. This can lead to a high noise level.
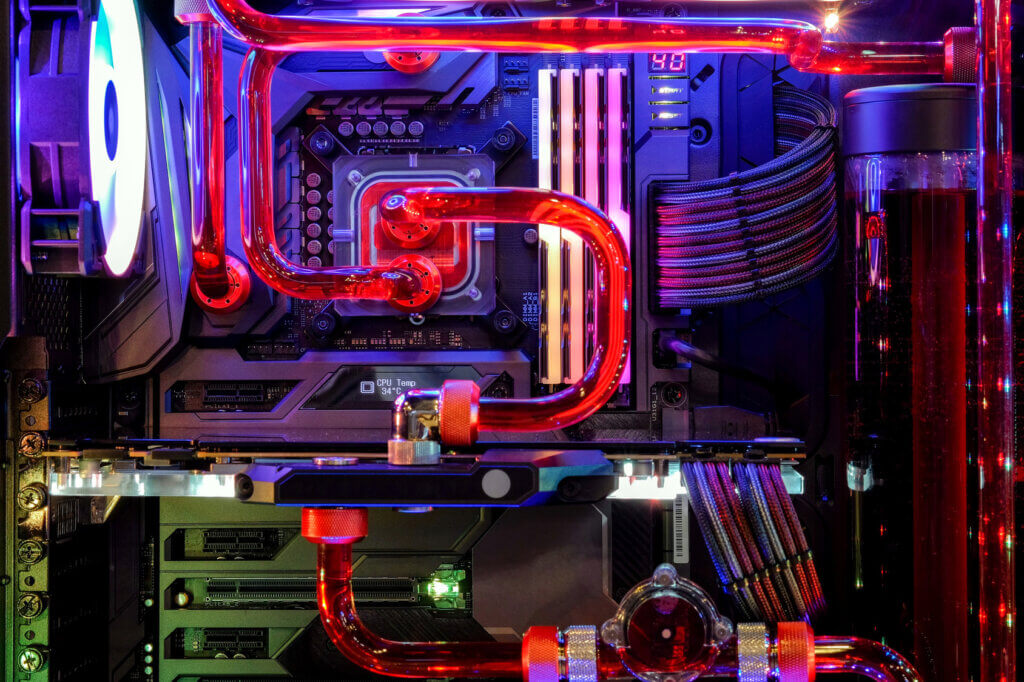
In some cases air cooling is no longer sufficient, as the components overheat anyway. In order to avoid damage, the computer may interrupt the game in progress or shut down completely. It can only be switched on again when the components have cooled down. For gamers who are in the middle of a game this is, of course, a disaster. The solution is water cooling. Here, the components are kept cool by a closed water circuit and a pump. Users can choose or design these systems in a colorful way. But be careful: inexperienced users should not install such a system themselves. In the event of a leak, there is a risk of liquid escaping and damaging hardware.
Power supply unit
The power supply unit is responsible for supplying the entire PC with power. It is connected to the mainboard, which distributes the energy to the hardware. Since gaming PCs often have energy-intensive high-end components, an ordinary office PC power supply is not sufficient. To ensure a sufficient power supply, a model with a total output of between 500 and 700 watts is recommended. Here, too, consumers should keep an eye on the noise level: in the meantime, many manufacturers offer specially insulated ‘silent’ power supply units.
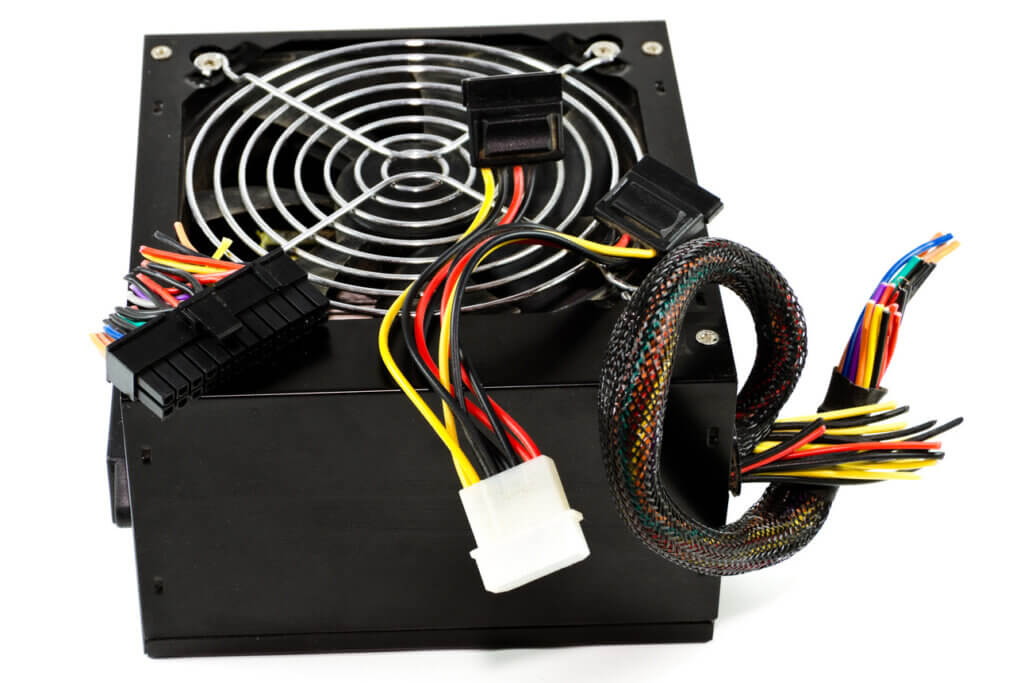

Energy consumption
How much power a gaming computer consumes varies. On the one hand, the basic power consumption of the installed hardware components plays a role, but so does the actual computing effort that the components perform when processing demanding gaming titles. The wattage consumption under full load differs greatly from the consumption in idle mode, i.e. when the system is simply running without the hardware being stressed by computationally intensive software. Office programmes or surfing the internet is hardly demanding but a game in full HD or even 4K graphics can increase the consumption to a total of 400 watts and more. When buying, gamers should make sure that the graphics card and processor are comparatively energy-efficient. Otherwise, there is a risk of unpleasant surprises when it comes to the annual electricity bill.
Connections: type and number determine connectivity
A good gaming PC should have a certain number of modern interfaces so that owners can connect as many different peripheral devices as possible, such as monitors, mice, USB sticks, or even a 3D printer. We present the most important connections.

DVI: digital image transmission
The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a standardized interface for transmitting image signals from a graphics card to a monitor. It replaced the old, analogue VGA interface. One disadvantage is that audio signals cannot be transmitted. Therefore, the DVI interface is gradually being replaced by the newer DisplayPort.

HDMI: the all-rounder
The High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) transmits both image and audio signals in high quality. HDMI cables have become the standard for connections between PCs, gaming consoles, mobile devices, and televisions. There are different sizes to consider: there is the comparatively large ‘normal’ HDMI plug but also the tiny micro-HDMI plug.

DisplayPort: the new standard for image and sound transmission
DisplayPort is a fairly new standard for transmitting image signals from a computer or laptop to a monitor. The advantage is that free channels in the cable can be configured for different purposes. As a rule, they are used for audio transmission. However, uses such as USB-C functionality for data transmission (up to 40 Gbit/s) are also possible.

USB 3.1: widely used all-rounder
The blue-colored USB sockets indicate the fast data transfer standard 3.1. These ports are downward compatible, so they can also be used with older USB sticks that only support the slower 2.0 standard. There should be at least four of these ports, but preferably six or eight, so that as many peripherals as possible, such as mice, keyboards, printers, 3D printers, or webcams, can find a slot.

3.5 millimetre jack: traditional audio transmission
The analogue jack connection is still widely used. Gamers can connect speakers and headphones to the gaming computer via this interface. However, it is associated with certain losses in quality. If there are several of these jack connections, the interface is suitable for connection to a 5.1 sound system, for example.

TOSLINK: digital audio transmission
Unlike the 3.5 millimeter jack, which is slowly becoming obsolete and increasingly rare, especially in mobile devices, the TOSLINK interface ensures loss-free digital audio signal transmission.

Ethernet: wired internet connection
The Ethernet interface enables the connection of a LAN cable to the computer. In this way, users can establish a wired internet connection that is less susceptible to interference and fast. For most gamers, a wireless connection via WLAN is out of the question due to speed losses and higher ping times. It should be a modern gigabit LAN interface with a maximum data rate of 1,000 Mbps.
Finding the right gaming PC
How powerful the individual components of a gaming PC should be depends on the type of user. Of course, the highest graphics settings are a dream for all gamers, but the high prices of the hardware required for this force the majority of interested parties to compromise on performance, resulting in different target groups.
In general, the following has to be said: the graphics card is the ‘heart’ of a gaming PC. Gamers who are putting together a new gaming PC should buy one at about a third of the total price of the PC. If the total budget for a new gaming PC is $1,500, for example, then the graphics card can be $500.
Browser gamers: $400 or less
Prospective buyers who like to play browser games like Mah-Jongg, Candy Crush, or FarmVille exclusively do not need a high-priced computer with special performance features. A relatively simple PC in the lower price range is sufficient. A reasonable graphics chip or a mid-range graphics card should be enough to enable smooth graphics.
Casual gamers: $400 to $750
This category includes gaming beginners and users with a limited budget. Fans of simple simulation games, for example, such as a farming simulator, also get their money’s worth in this price range. Since such gamers do not have huge expectations of the graphical presentation of their game titles, it is also not necessary to upgrade their systems at regular intervals by installing new components. Of course, users can also do office work on these computers. However, such PCs become outdated very quickly.
For this target group, the Intel processors of the i3 and i5 series or AMD’s FX models are ideal. In terms of graphics, a card from the Radeon R5 series or the GeForce 1030 series can provide the necessary computing power. For such a system, we also recommend a RAM of eight gigabytes and a terabyte of HDD hard drive storage, which offers enough space for applications and games.
Core gamers: $750 to $2,000
For users in this category, a current processor from the i5 to i7 or Ryzen 5 to Ryzen 7 series is recommended. In terms of graphics performance, it may be a card that is roughly in the performance range of a GeForce 1660 Ti or Radeon RX 590. It goes without saying that this range extends both upwards and downwards and that a significantly more powerful GeForce 2070 can also be considered. Current adventure games can also be played with such a system. However, compromises have to be made with the graphics settings. Thus, the card still operates smoothly at the detail level “high”, but is overtaxed at ‘very high’ or ‘ultra’. Furthermore, gamers in this segment should expect 8 to 16 gigabytes of RAM and a hybrid storage with about 2 terabytes of HDD and 100 gigabytes of SSD.
Owners of such gaming PCs enjoy games in full HD resolution. But these models can do much more: creative work that requires comparatively high computing power such as image and video editing is no problem with such PC. This kind of computer will remain relevant for several years.
High-end gamers: $2,000 or more
This type of gaming system is suitable for a comparatively small group of enthusiasts for whom 4K graphics at the highest level of detail in the game settings are important. They do not want to accept any performance losses. That is why they also accept very high acquisition costs. They have monitors that are around 28 inches in size. Widescreen monitors are also popular, and they can even reach the four-digit dollar mark in terms of price. This demographic includes enthusiasts, YouTubers, e-sports pros, and streamers.
The processor needs a correspondingly high performance: if it is from Intel, it must be a modern i7 or preferably i9 processor. With AMD, only the new Ryzen 7 or Threadripper can be considered. The graphics performance is provided by an Nvidia GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, a GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, or an AMD Radeon Pro Vega 16 GB, for example. These high-end graphics cards alone cost between §500 and §2,000, depending on the equipment. Some particularly demanding gamers treat themselves to two graphics cards in a so-called SLI bridge in their computer. Their computing power is extremely high, but sometimes individual game titles have problems recognizing or utilizing SLI combination graphics cards: in this case, a RAM with 32, or better, 64 gigabytes of memory is appropriate. Hybrid memory with up to 6 terabytes total capacity ensures that there is never a shortage of memory.
Useful accessories for gamers
Users can choose from a wide portfolio of accessories to enrich the gaming experience. We list a few ideas.

Gaming keyboard: with special functions
Gaming keyboards are characterized by their high quality and functionality. They often come with additional features such as backlighting, USB interfaces, or special keys that are either preset or can be individually configured by the user.

Gaming mouse: additional buttons
A gaming mouse is essentially characterized by a high sampling rate of the optical sensor. The very high precision achieved in this way provides a decisive advantage in many computer games. With the additional buttons, users can lower or increase the sampling rate as needed so that the mouse pointer on the screen reacts slowly or sensitively to the player’s hand movements as desired.

Gamepads: console feeling on the computer
In many action-adventure games, the binary movement commands of keyboards are not sufficient for natural-feeling movement, for example when changing from slow, careful movement speed to normal or fast movement speed – the arrow keys of keyboards only offer the options ‘press key – go’ and ‘release key – do not go’. In addition, many titles on the PC are first and foremost optimized for the mass market of consoles, so developers don’t try too hard to make keyboard controls comprehensive. What is more, many players quickly get lost on the keyboard in games with extensive key assignments, so that the controls do not feel intuitive. The ergonomics and clear arrangement of a gamepad is associated with far fewer incorrect keystrokes for most players, even in the case of multiple key assignments. A classic example of a game that makes a gamepad indispensable on a gaming PC is the famous football simulation FIFA. With gamepads, several players compete against each other for exciting games — whether with friends on the sofa or online against other players worldwide.

Monitor: window to virtual worlds
A good monitor with a fast refresh rate is important for a true-color gaming experience. The choice of whether the monitor should support Full HD or even 4K resolutions depends on the type of gaming computer and the gamer’s wishes and budget. Special curved monitors convey a particularly wide field of vision and thus the feeling of being in the middle of the action. Especially in shooters, a fast response time is crucial.

Office chair: the right sitting position
Sitting on an unsuitable chair for a long time is not only uncomfortable, it can also hurt worsen your posture. A back-friendly chair with lumbar support ensures users a favorable sitting position over longer periods of use. Models with a modern design are also marketed as gaming chairs. These are visually very similar to the seats of racing cars. Even with a good gaming chair, however, you should pay attention to your sitting posture. Chairs cannot fix a sloucher.

Sound: speaker or headset
Computer gaming without sound is unthinkable. The range of speaker systems starts with the classic two-way speakers with or without subwoofer and extends to 5.1 and 7.1 systems and large smart home systems connected to the home network and spanning several rooms. For users who need to be considerate of roommates or neighbors, a variety of headphone and headset solutions is available. This offers even more advantages, such as excellent directional surround sound, precise enemy locating in competitive shooters, and the possibility of voice chat via an integrated microphone.
Building your own gaming PC
In addition to the option of purchasing a fully assembled and installed gaming computer, interested buyers have the option of specifically assembling individual components and installing them themselves. The purchase of a gaming laptop is also an alternative worth considering for some users.
Assembling a computer yourself: a cost-saving option
Those who do not buy their PC ready-made but select, order, and assemble all the components themselves usually save a lot of money compared to buying the whole thing. However, this requires both manual dexterity and a minimum of technical expertise. Users must be careful when installing the components so as not to damage them. They must also find out in advance whether the components harmonize with each other and do not slow each other down.
Furthermore, if the computer does not run smoothly or does not start at all, there is no guarantee or warranty. Both are limited to the functioning of the individual parts, but not to the stability of the PC as such. In that case, users would either have to get help from a third party, possibly even from a specialist shop for a fee. Thus, a computer assembly kit is only recommended to experienced users.
Advantages
- Usually cheaper to purchase
- Choice of each hardware component
Advantages
- Components can be damaged during assembly
- Computer may not function properly after assembly
- Components that do not harmonize can lead to bottlenecks
- Not immediately ready for use
Users who don’t want to deal with the assembly, as well as beginners, are therefore better off with a complete system. Here everything is pre-assembled and in many cases the operating system is already pre-installed. The gaming computer is then immediately ready for use.
Gaming laptop: mobile high-end gaming experience
In principle, a gaming laptop can do exactly the same as a desktop PC. However, it may be more cumbersome to operate. The big advantage: users are not tied to one location, mobile gaming and working is possible everywhere. A major disadvantage is that buyers have to spend a lot more if they want to get the same performance as from a gaming PC. In addition, a laptop with its limited space is more difficult to upgrade.
Advantages
- Flexible in the choice of location
Disadvantages
- Powerful components more expensive than for desktop computers
- External input devices may be necessary for comfortable operation
- Few options for upgrading
Care and maintenance
Over time, dust accumulates inside the computer and is transported into the interior via the casing fans. This can lead to component wear, ventilation path blockage, and, as a result, increased heat generation. You can tackle these issues by shutting down the computer, unplugging the power cord, opening the casing, and carefully vacuuming dirty areas with a brush attachment. Take great care to secure or remove loose components, otherwise they could suddenly disappear into the suction pipe. If necessary, also reduce the suction power. Fine brushes or an air pressure spray further improve the result. An annual cleaning is already enough to keep the PC in good shape.
Another type of spring cleaning you should do as a user of a gaming PC is software-based: always keep system and graphics card drivers up to date. As a rule, the software of graphics cards will notify you as soon as an update is ready for installation. However, you can also check manually on the manufacturer’s website. In addition, practical shortcuts are arranged in many graphics card softwares, which start the update process when clicked. Using the latest version of the graphics card driver reduces the risk of errors and system crashes. Moreover, graphics card manufacturers develop specially optimized driver versions for many new major game releases to ensure that these titles can be played as smoothly as possible. Updating the operating system and anti-virus software prevents the computer from being compromised by malware and data from being stolen or encrypted.
Image 1: © Sebàstian / stock.adobe.com | Image 2: © Andrey Armyagov / stock.adobe.com | Image 3: © V'yacheslav Partola / stock.adobe.com | Image 4: © elmar gubisch / stock.adobe.com | Image 5: © Victoria / stock.adobe.com | Image 6: © FinalCheck | Image 7: © RuslanKphoto / stock.adobe.com | Image 8: © chiradech / stock.adobe.com | Image 9: © yurchello108 / stock.adobe.com | Image 10-12: © FinalCheck











 229 reviews
229 reviews