Printer purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What you need to know
- Multifunction printers with copying and scanning functions are equally suitable for office and home use.
- Depending on the purpose and frequency of use, either inkjet or laser printers are recommended.
- Thanks to a wide range of connectivity options, printers can be operated and controlled in different ways.
- Special functions such as duplex printing and page feed largely automate the work with modern printers.
- Anyone who buys a printer should keep an eye on the follow-up costs for ink and toner in advance.
The all-rounder for office and home
You may think that printing documents in the age of digitalization is a bit out of date. But far from it: Even though a paperless future is highly anticipated for efficiency and environmental reasons, the annual print volume in companies and private households remains at a high level. A letter to the authorities, for instance, cannot always be replaced by an e-mail, important documents are still filed in printed form, and worksheets are necessary for school and studies.
What we call “printer” today, however, is actually much more than that. The devices can no longer just print, but they offer a range of different functions, like digitising documents by scanning and copying them. Accordingly, these devices are not merely printers, but so-called multifunction printers or all-in-one printers.
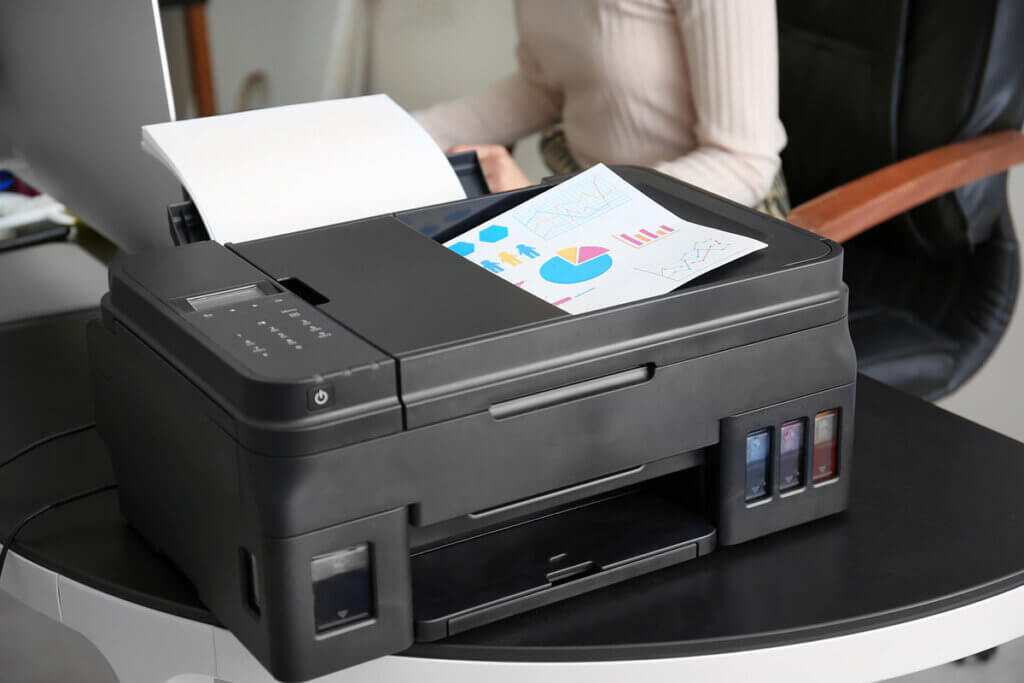

Multifunction printers are all-purpose tools for the office or home. They combine at least three functions — printing, scanning, and copying — in one compact device. In this case, they are called 3-in-1 multifunction printers. There are also 4-in-1 devices that offer an additional fax function.
A printer for each purpose
Depending on the number of users, frequency of use, and primary application, a different type of printer is recommended.

Photo print
Amateur photographers often want to print high-quality pictures on special paper with great color depth. However, buying a printer with only this one function can be rather inefficient. Instead, they could use an inkjet multifunction printer that is optimized for photo printing with five separate ink cartridges. Here, spending a few extra bucks might be a good idea, as inexpensive models rarely deliver the necessary quality. Laser printers cannot be considered in this case, as they cannot print on photo paper.

Text print
Laser printers promise sharply contoured letters without color gradients and fast printing speeds. They are, therefore, a great choice for the office. When using cheaper printer paper, inkjet printers show slight color fringing. Laser and especially LED printers can handle larger print jobs much more quickly than inkjet models. In addition, the toner range exceeds that of a conventional ink tank by far.
Text with illustrations
Anyone who regularly prints texts that include images or other visuals should go for an inkjet-based multifunction printer. These are the most popular devices, especially for home use, as they are rather versatile. Higher-priced models now achieve good results at high printing speeds, so they are also becoming increasingly popular in smaller offices, even competing with laser printers.
Rare use
If you only print sporadically and at irregular intervals, you should go for a laser printer. If you do not use an inkjet printer for a long time, the ink will dry out eventually. In this case, the printer nozzles will have to be cleaned with each use, resulting in increased ink consumption and thus high follow-up costs.
To make your purchase decision easier, let’s take a look at a concrete example: Private users, for example families with school-age children, usually have a relatively low printing volume. The printer has to handle small print jobs a few times a week, mostly text documents — in some cases with illustrations — and now and then a high-quality photo. Occasionally, documents also need to be scanned or copied. For this user profile, multifunction printers with inkjet-based printers are best suited. Those who value high-quality photo printing should look out for an additional pigment black ink cartridge.
If, on the other hand, you can do without photo printing altogether and rarely use the printer, you should go for a multifunction laser printer. Laser printers are also recommended for larger offices where numerous large print jobs are performed regularly.
What printing technologies are available?
Commercially available printers and multifunction devices are based on one of three different printing technologies:
- Inkjet printing
- Laser printing
- LED printing
Each of the printer technologies offers different advantages and disadvantages. If you want to buy a multifunction printer, you should know these beforehand and choose the technology that best meets your individual requirements.
Advantages and disadvantages of inkjet printers
Advantages
- Low purchase price
- Now almost as fast as laser printers
- Good quality photo printing
- Special media such as photo paper, foils, or CDs can be printed on
- Borderless printing possible
- Low power consumption
Disadvantages
- Ink may fade
- Higher cost per page
- Higher follow-up costs for ink
- Ink can dry out
- Slower than laser printers
Advantages and disadvantages of laser printers
Advantages
- Sharp contoured text print
- Printout UV- and water-resistant
- Low printing costs
- High printing speed
- Toner does not dry out
- Long service life
Disadvantages
- Larger than inkjet printers
- Less contrast and color depth in image printing
- More expensive to buy
- Higher energy consumption
- Toner may peel off
- Fine dust emission
- No borderless printing
- Heat-resistant paper needed
Advantages and disadvantages of LED printers
Advantages
- Fastest printing technology
- Similarly compact to inkjet printers
- More stable due to lack of moving components
- Sharp print in margins
Disadvantages
- Color space and contrast levels in photo printing worse than in inkjet printing
- Less contrast and color depth in image printing than inkjet
- Highest purchase price
- Capacity exceeds demand in home use
- Higher energy consumption
- Toner may peel off
- No borderless printing
- Heat-resistant paper needed
Other printer types
In addition to the conventional printing technologies used in multifunction printers, there are other printing technologies that are used for special applications.
Photo print
There is no single definition for the term photo printer. In essence, any printer that can print photos in high quality is also a photo printer. They offer a high resolution and the possibility to create borderless prints in the usual photo formats.
The printing technology of photo printers is not set in stone. For instance, they can be high-quality inkjet printers. These printers are compact and work independently of a computer. Via an integrated display, the user controls tools for image processing and optimizes images with special ink on photo paper before printing. These printers are not recommended for printing ordinary text documents.
Dye sublimation printers, which achieve a particularly impressive color depth and saturation, are also recommended for photo printing. The mode of operation is similar to monochrome thermal transfer printing, which is used in automatic pay stations or ticket machines. Dye sublimation printers heat dye wax to 572 to 752 °F and steam it onto the photo paper with pixel precision.
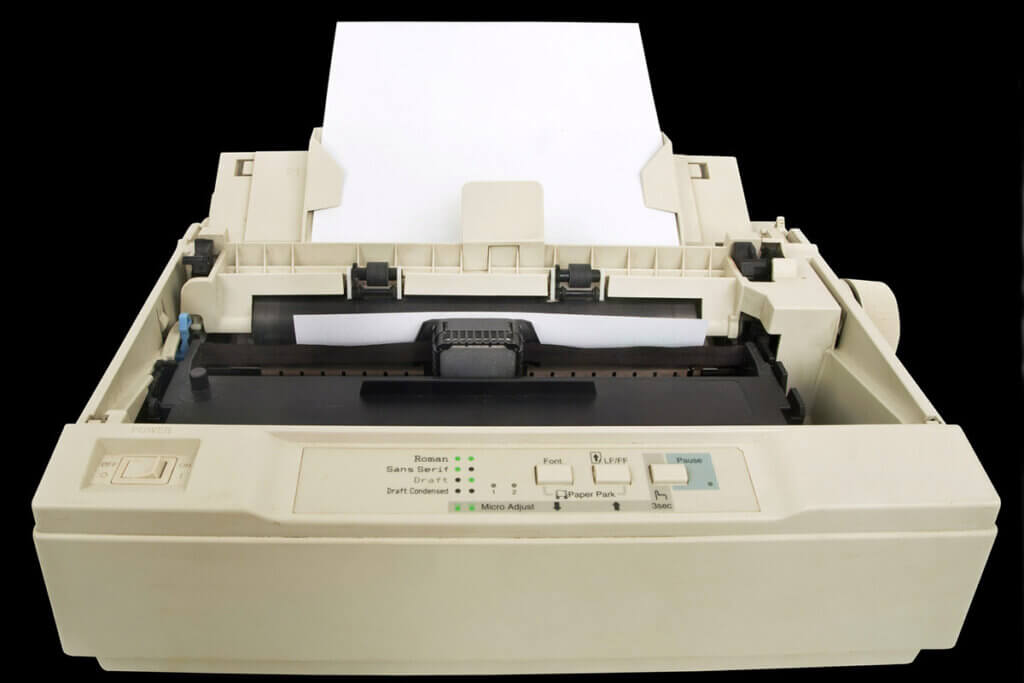
Dot matrix printing
Dot matrix printers are considered to be particularly robust and reliable, but they are rarely found nowadays. They are still used occasionally in companies, doctors’ offices, banks, or in the form of receipt printers. In terms of quality, they cannot compete with modern inkjet or laser printers.
Between 8 and 48 needles strike through a ribbon in the dot matrix printing process, transferring the image dots to the printer paper. The matrix of pixels creates the printed image. These are so-called impact printers that exert physical pressure during the printing process. This makes dot matrix printers ideal for producing carbon copies.

What to look for when buying
The printing technology may be the most important purchase criterion to consider when buying a printer. However, there are multiple other factors to consider when choosing the right model.
Resolution
The print resolution provides information about the best possible quality of the printouts. Manufacturers specify it with the unit “dots per inch (dpi)”. For sharp printouts of text documents with a laser printer, 600 x 600 dpi is more than enough. If you want to print pictures and color images, you should choose color laser printers with a resolution of at least 1200 x 1200 dpi.
For inkjet printers, the resolution should generally be higher, especially if the user also wants to use the device for printing high-resolution photos. Inkjet printers optimized for photo printing often have 4800 x 1200, 5760 x 1440, or even 9600 x 2400 dpi, according to the manufacturer’s specifications. But are such high values really necessary?
Caution with resolution specifications!
High values such as 9600 x 2400 dpi are usually values calculated by interpolation. To compare the specs with those of a laser printer, the physical resolution must be taken into account. Unfortunately, this is rarely specified by the manufacturers.
The fact is that 2400 x 2400 dpi is sufficient to reproduce a polished art print in the best possible way — provided the highest resolution is selected in the print menu and high-quality ink and paper is used.
After all, resolution is by no means everything: ink and paper play just as big a role in the quality of the printouts! For multifunction printers with a scan unit, it is not only the print resolution that matters, but also the scan resolution. If you scan a lot, you should make sure that the scan resolution is high enough even at standard settings. Increasing the resolution in the scan menu leads to a longer scanning process.

Speed
Print speed and scan speed are measured in pages per minute. A higher page throughput typically leads to a higher purchase price. If you do not have to handle numerous large print jobs regularly, you can save some money here. While the print speed of laser printers is identical for color and black-and-white prints, inkjet printers need more time for a color print than for a black-and-white print.
With inkjet printers, it is above all the number and arrangement of the nozzles that determine the printing speed. In black-and-white printing, many good inkjet printers now compete with laser printers. However, the information on page throughput always refers to specially configured test pages at a low resolution. Elaborate photo prints with higher resolution take considerably longer.
Functions and features
Printers now have a number of functions that automate printing, scanning, and copying to a large extent, and make operation much easier.

Printing on both sides (duplex)
Double-sided printing is, of course, possible with any printer if the user manually turns the sheet after printing and reinserts it. With the “double-sided printing” or “duplex printing” function, this is done automatically. After printing on the front side, the machine retracts the sheet and prints on the back side. This saves time, paper, and energy. If you print a lot, you should opt for a model with this function.

Display
Not every printer model is equipped with a touchscreen yet, but the trend is clearly moving in the direction of being able to control the devices directly via the display. With a touchscreen, it is particularly intuitive and easy to adjust all settings, define print areas and issue print, scan or copy commands. A print preview on the display is particularly useful for work steps such as scanning or copying, as you do not have to use your PC or a mobile device with it.

Borderless printing
Brilliant and clean photo printing in any format is only possible if the printer is capable of borderless printing. For technical reasons, this feature is almost exclusive to inkjet printers. Many models do allow borderless printing for smaller formats, for example the common photo formats 15 x 10 or 13 x 9cm. However, devices that can also print borderless in A4 format are rare.
Document feeder
You might be familiar with the automatic document feeder (ADF) through copy machines. Nowadays, it is mainly multifunction printers that have such a function. The user places a stack of documents to be scanned or copied in the feeder tray, and the device automatically processes the documents one after the other. When digitising analogue documents or larger copy jobs, this is a real time-saver, as you can do other things while the machine is doing the work. However, users should pay attention to the maximum capacity of the ADF to not overload it.
Format and capacity
How much paper fits in the printer? Which paper format is the right one? If you print a lot, have large print jobs to handle, or want to print in formats larger than A4, you should pay attention to these specifications when choosing a printer.
Format
The standard size of printers and multifunction devices allows printouts up to A4 format at most. Smaller formats, especially A5, are always supported. If you also intend to make printouts in A3, you should go for an A3 capable printer. Inkjet A3 printers are nowadays of a similar size to A4 printers. As multifunction printers, however, they are usually only available as 3-in-1 versions without a fax function.
Paper capacity
The paper capacity defines how many sheets of plain paper the printer can hold in the paper input tray as a paper supply. The specified number of sheets refers to paper with a recommended thickness. If you want to use thicker paper, you must reduce the number of sheets accordingly. Printers for home use usually have a capacity of 60 to 250 sheets.
Many laser and LED printer models allow an additional paper tray to be added at a later date. Caution is advised with inkjet printers: Some manufacturers specify a “media capacity” instead of a paper capacity. Inkjet printers often have separate trays for plain paper, small-format photo paper, CDs, and transparencies. The indication of the total media capacity is therefore the sum of the capacities of all individual trays, not just the capacity of the paper feed tray.
Attention, paper jam!
If the printer refuses to work, there may be a paper jam. This is one of the most common problems with inkjet and laser printers. Many devices detect this automatically and show an error message via the display.
To clear the jam, first try slowly pulling the paper out of the printer by hand. If it is stuck or about to tear, switch off the printer, unplug it from the mains, open the cover, remove any cartridges or toner, and check whether there are any paper remnants hanging between the feed and guide rollers. Remove these remnants if necessary.
After you have cleared the paper jam, you should restart the printer. To prevent jams, it is advisable to use only suitable paper, not exceed the specified paper capacity, and load the paper correctly.
Connectivity
Nowadays, you don’t necessarily have to wire a printer to a computer. The devices offer a wealth of different connection options that allow the device to be integrated into a smart network.

LAN and WLAN
Instead of connecting a printer to a PC, it is possible to plug it into a network router via LAN cable or via WLAN. Then, all computers and mobile devices in the local network can access the printer. While the WLAN connection prevents annoying cable tangles, a LAN connection is more stable and faster, but this is of little consequence in normal home use.

Wi-Fi Direct
Wi-Fi Direct capability is now standard on new devices. Data is transmitted from a computer, mobile device, or digital camera directly to the printer without the need for a router or hot spot. Wi-Fi Direct-capable devices are themselves the base station. A laptop or PC is therefore no longer necessary to control the printer. Users control the printer from their smartphone or tablet via the manufacturer’s own app or a third-party app.
USB and SD
A USB port and SD card slot are useful for users who want to print directly from a USB stick, external hard drive, or SD card without having to cache the data via a PC or cloud. The selection of the corresponding documents is possible via the printer control or the touch display.

NFC
Near-Field Communication (NFC), i.e. wireless communication via electromagnetic induction, is mainly known from contactless payment. Laser printers, in particular, which are also suitable for use in the office, also offer the option of enabling the printer via NFC, for example using a chip card. It is also possible to transfer print jobs from the smartphone to the printer via NFC.

Bluetooth
A Bluetooth interface on the printer offers another option for controlling the printer without a cable connection. As long as the user is near the printer, they can easily send print assignments from a laptop, smartphone, or tablet via Bluetooth.
Airprint
AirPrint, developed by Apple, offers the possibility to print wirelessly over the network from mobile devices with iOS.Any file formats that can be opened with the iPhone or iPad can be printed via AirPrint, provided the printer supports this function.

Google Cloud Print
Cloud-enabled printers are connected directly to the internet and can be registered with Google Cloud Print without a PC or laptop. Once registered, the user can manage the printer, check ink levels, and send print assignments to the printer from anywhere via any internet-enabled device.

App
Every printer manufacturer now offers its own app to control the printer. Some examples are Epson iPrint, HP ePrint and the HP Smart App, the Canon PRINT Inkjet/SELPHY App, the Brother iPrint&Scan App, or Samsung Mobile Print.
Purchase price and follow-up costs
The purchase price of a printer depends on various factors:
- Printing technology
- Print speed
- Print resolution
- Additional functions
- Number and bandwidth of connectivity options
A household that prints infrequently can save money when choosing a printer by opting for a model that is not quite as fast and foregoing any unnecessary additional features such as duplex printing or certain connectivity options. However, it should also be noted that the follow-up costs for ink, toner, and paper will have to be paid regardless.
Ink cartridges
Cheaper printers often turn out to be very cost-inefficient because the original cartridges from the manufacturer contain little ink and are outrageously expensive. There are three ways to avoid overly high ink costs:
- Get an ink subscription from the manufacturer’s line.
- Use cheaper alternative cartridges.
- Refill original cartridges or have them refilled.
Some printer manufacturers now offer ink subscriptions. With the HP instant ink subscription model, for instance, you pay a monthly fee based on your actual consumption, i.e. the number of pages printed. The printer automatically orders a new cartridge as soon as the cartridge runs out.
Often times, inexpensive ink from off-brand manufacturers hardly differs in quality from the original ink. However, the costs for alternative products can be up to 70% lower than those for original ink cartridges. It is worthwhile to compare alternatives yourself. However, you should make sure that the cartridges are actually compatible with your printer model.
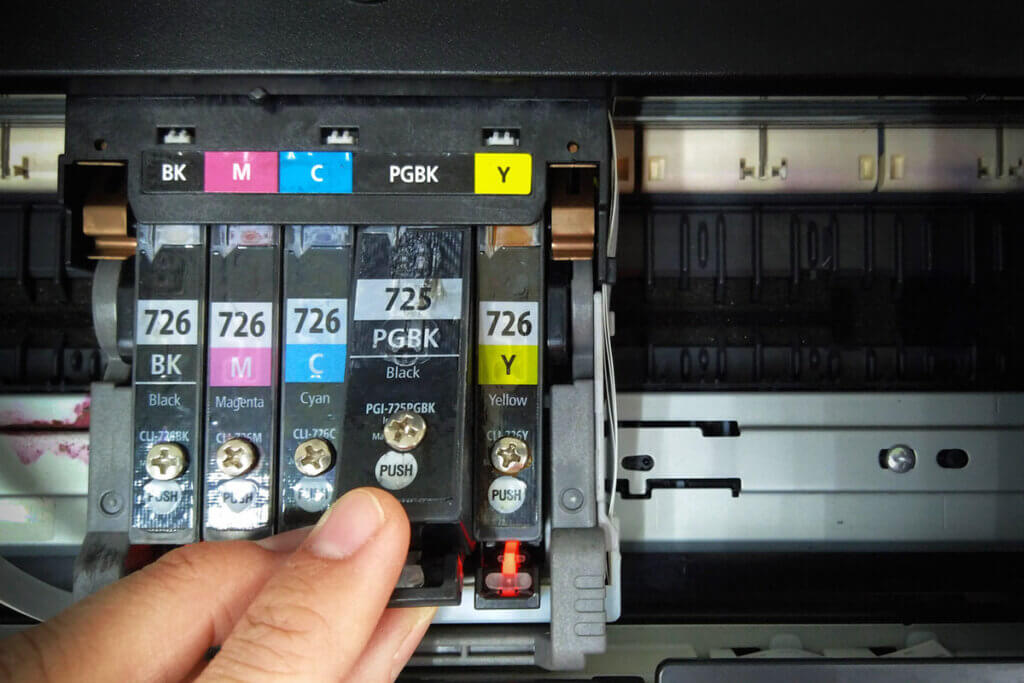

If you refill empty ink tanks yourself, you should make sure to reset the printer cartridge chip after refilling. The chip documents the fullness level of a cartridge and will not accept a refill on its own. Chip resets are usually included in refill packs. In the service of an ink filling station that offers refilling as a service, resetting the cartridge should be standard.
Reduce ink consumption
It is not only the printing itself that uses up ink in an inkjet printer. Every time the machine is switched on, it automatically performs a print head cleaning, which also consumes ink. Since modern devices consume little power in standby mode, it may be more cost-efficient to not switch the printer off completely. If print assignments only occur sporadically, it is advisable to collect a few and send them to the printer in one go.
The PC does not recognize the cartridge
After inserting non-proprietary cartridges, the PC may continue to display an empty cartridge and prompt you to change it. In this case, the cartridge has not been recognized. Make sure that the cartridge is suitable for use in your printer model, and clean the contacts of the cartridge with a cloth. If this does not work, you should remove all cartridges and disconnect the printer from the mains and from the PC. After some time, reinsert the cartridges, connect the machine and start it. If the problem persists, you should reset the chip.
How do printers work?
There are essentially two different printing technologies for ordinary home and office printers: laser printing and inkjet printing. In addition, there is LED printing, which is very similar in its mode of operation to classic laser printers. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages, which are based on its specific characteristics. Inkjet-based multifunction printers currently dominate the market because they are more popular with private users.
Inkjet printer
Inkjet printers are matrix printers. They produce a finished print image by placing closely spaced image dots. The inkjet printer places these dots through ink droplets that are shot from the nozzles of the print head and directed onto the print medium — usually paper. The print head with the inserted ink cartridges moves back and forth horizontally on a rail, driven by an electric motor and a toothed belt.
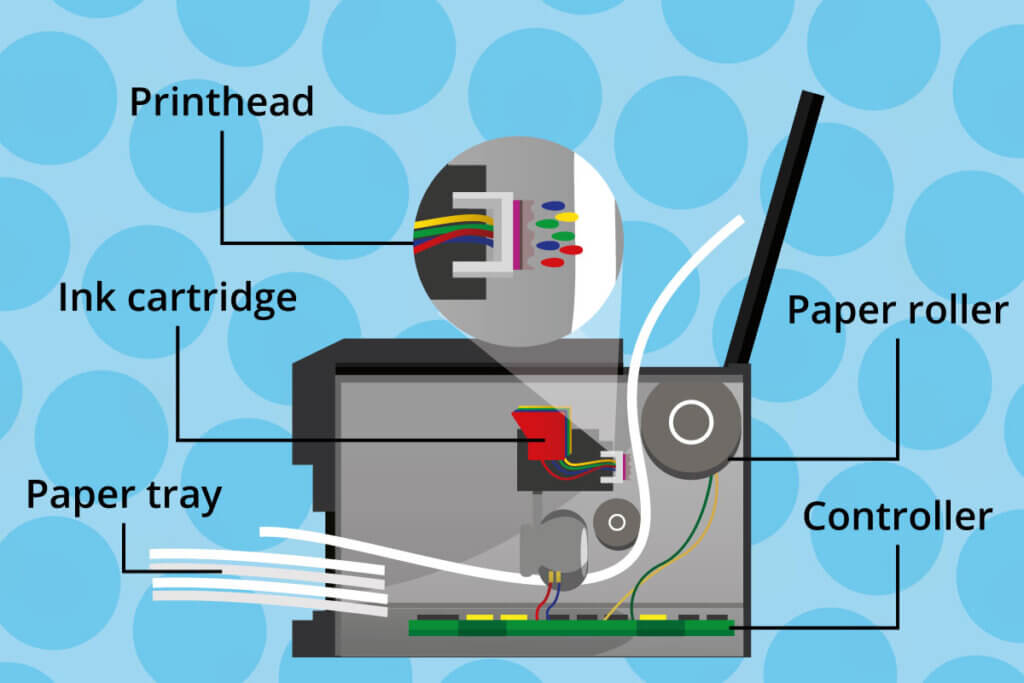
Another motor drives a roller that feeds the paper under the print head. The ink is applied to the paper line by line through the nozzles on the print head. The ink drops are produced separately by the print head according to the print pattern at hand and not continuously, which is why it is called drop-on-demand (DOD). The print head therefore does not come into direct contact with the paper. Therefore, inkjet printers are not only matrix printers, but also non-impact printers.
Non-impact printing
Abbreviated to NIP, “non-impact printing” refers to various printing processes that do not require a printing plate at all. In addition to inkjet printing, this also includes laser printing, thermal printing, and photography.
Different inkjet printer technologies
Printers that operate on the basis of DOD inkjet printing can be divided into two groups based on the technology used to drive the ink out of the nozzle: BubbleJet and piezo printers.
In BubbleJet technology, a heating element heats ink droplets, causing them to expand and inflate. This creates a vapor bubble that catapults an ink droplet through the nozzle under high pressure. BubbleJet technology is used by some leading manufacturers, like
- Canon,
- HP,
- Lexmark.
Epson inkjet printers, on the other hand, are so-called piezo printers. These use the inverse piezoelectric effect, in which piezo crystals in ceramic elements are pulsed with electrical voltage. This technology is said to produce more uniform and sharply contoured droplets and to be more durable than the BubbleJet printers.
Laser printer
Unlike inkjet printers, laser printers are not matrix printers but page printers. They print an entire page in one pass. They use the so-called electrophotography or xerography process (named after the company Xerox which invented the technology), which is also used in photocopiers. An image drum covered with a light-sensitive layer, the photoconductor, is negatively charged electrostatically by applying an electrical voltage.
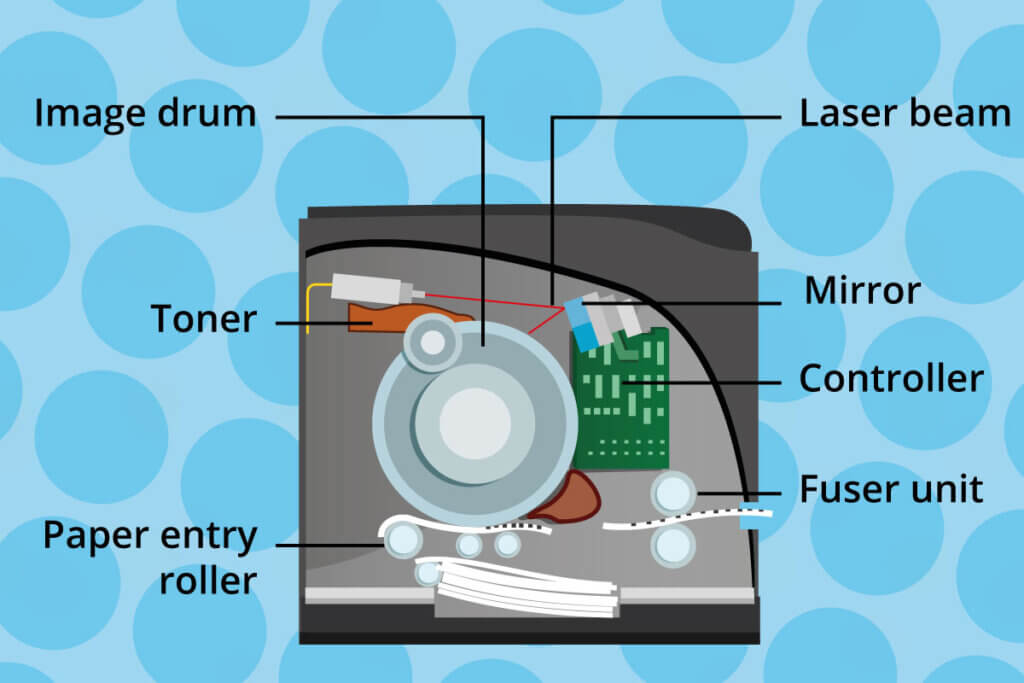
A movable mirror directs a laser beam specifically to the spots on the photoconductor the toner needs to get to and releases the electrostatic charge. The image drum rotates further to the toner cartridge, where toner is transferred to the erased areas of the photoconductor. Since the toner has the same charge as the photoconductor, it only gets to the erased areas.
The photoconductor then rolls over the printer paper. A positive voltage is applied under the paper, which causes the toner to transfer onto the paper. Finally, the toned paper passes through the fuser unit, where the toner is permanently fused with the paper at around 356 °F.
LED printer
The way LED printers work is similar to that of laser printers — in fact, LED printers are often even referred to as laser printers. One difference, however, is that LED printers do not need a mirror construction because they do not transfer dot by dot with a laser, but entire lines in one go with a row of light-emitting diodes onto the photoconductor. Thanks to this single-pass technology, LED printers can transfer all colors to the paper in one step, whereas conventional laser printers need one pass per color. As a result, LED printers work faster than laser printers.
Image 1: © Africa Studio / stock.adobe.com | Images 2-5: © FinalCheck | Image 6: © burnel11 / stock.adobe.com | Image 7: © NewFabrika / stock.adobe.com | Images 8-19: © FinalCheck | Image 20: © jakkrit / stock.adobe.com | Images 21-22: © FinalCheck




















 6,051 reviews
6,051 reviews



