OLED TV purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- OLED TVs are characterised by their organic light-emitting diodes, which make each pixel its own light source.
- They offer strong contrasts, true black, brilliant colours and even illumination.
- OLED screens are available in 55, 65 and 77 inch sizes. In addition, consumers choose between flat-screen TVs and curved models.
The new generation of TVs
Clunky tube TVs with pixelated pictures have long been a thing of the past. Modern flat-screen models are getting thinner and thinner, and their picture quality is no longer comparable to that of earlier TVs. Even inexpensive LCD TVs usually deliver a very good picture. The royal class among televisions is currently formed by so-called OLED TV sets, which began to conquer the market a few years ago. While the first TVs with OLED technology were hardly affordable for ordinary consumers, there are now also cheaper models.
Find out what OLED actually means and what advantages TVs with this technology have in our comparison of the best OLED TVs. We also tell you what you should look out for when buying, what distinguishes OLED models from different manufacturers and where you can find further tests.
What is OLED?
Most current-generation flat-screen TVs use one of the following two technologies to display the picture:
- LCD
- OLED
The differences between OLED and LCD
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens, often called LED screens, have a layer of liquid crystals, hence the name. Each liquid crystal represents a pixel and acts like a colour filter. Depending on the orientation, the crystals let more or less light through. To create an image, the liquid crystals are illuminated either by LEDs coming out of the corners or by fluorescent tubes directly behind them.
Beaten to the punch: plasma TVs
Besides LCD and OLED, there is a third technology in televisions: plasma. The picture quality of plasma TVs is just as high as that of OLED TVs and a little better than that of LCD sets. However, the production costs for plasma TVs are so high that they do not justify the small quality advantage over LCD models.
No backlight
Unlike LCD technology, the OLED version does not require a backlight. The pixels here are not produced by liquid crystals, but by organic LEDs (OLEDs). These organic light-emitting diodes consist of carbon compounds. They generate light and colour themselves. While LCD TVs illuminate large areas, in OLED TVs each pixel is itself a light source. To display a black pixel, the corresponding OLED simply stays off.
Deep black and strong contrasts
OLED TVs can display very sharp contrasts and a perfect black. Here, LCD TVs are at a clear disadvantage. Because entire areas of the screen are illuminated, they cannot display true black. Dark areas here are also always slightly illuminated and do not look as dark as they should. In contrast to the rich display on an OLED TV, the dark areas of the picture look as if they are covered by a veil of grey. In contrast, with OLED technology, all pixels function independently of each other in terms of their brightness and colour representation. This allows OLED TVs to optimally reproduce true black, sharp dots and edges.
Uniform illumination, fast response times and brilliant colours
Likewise, the organic light-emitting diodes enable an evenly illuminated picture. Unlike LCD TVs, viewers get the same good picture at any angle they face the screen. In contrast, users of LCD TVs have to reckon with colour and brightness fluctuations when they look at the TV from the side.
In addition, the self-luminous OLEDs generally have a stronger luminosity than the liquid crystals of LCD screens, which are illuminated from the background. This allows OLED TVs to display brilliant colours. Another advantage: the organic light-emitting diodes react particularly quickly to picture changes. This means that OLED TVs can display fast movements, for example in an action film or during sports broadcasts, without any blurring being visible when the picture changes.

Ideal for gaming and home cinema
With their short response times and good motion sharpness, OLEDVs are ideal for demanding gamers. Some models, for example the Panasonic FZW954, even have a special gamer mode that reduces the processing time of input signals to a minimum.
OLED TVs are also ideal for home cinema. Film and series fans can enjoy brilliant colours, rich blacks and strong contrasts.
It could hardly be slimmer
The lack of backlighting gives OLED TVs an advantage over LCD sets not only in terms of picture reproduction. Because no additional layer of LEDs or fluorescent tubes is needed, flatter and lighter screens are possible. For comparison, two 65-inch TVs: the OLED model LG OLED65C8LLA has a screen depth of 4.7 centimetres, while the screen of the LCD TV PHILIPS 65PUS6503 is 8.8 centimetres deep. In addition, the OLED TV weighs 21 kilograms, which is 3.6 kilograms lighter than the LCD set (24.6 kilograms).
The possibilities of OLED
OLED technology also makes it possible to create bendable and rollable screens. This is not only interesting for the future of televisions, but also for smartphones and tablets. Samsung and Lenovo, for example, are already working on foldable and bendable smartphones.
What are the disadvantages of OLED models?
Of course, OLED TVs do not only have strengths. Unlike LCD sets, they can display true black, but they are weaker in terms of maximum brightness. Compared to its beginnings, OLED technology has already improved considerably in this respect. However, especially larger, bright surfaces, such as those used for winter sports broadcasts, usually still appear somewhat duller on an OLED TV than on a comparable LCD model. This is because more current would have to flow into the display than the small structures currently allow in order to display large-area, bright white.
OLED TVs are also still at a slight disadvantage in terms of picture reproduction in bright surroundings due to their lower brightness. So consumers have to weigh up the pros and cons: Brighter white and a better picture in bright surroundings, as LCD technology allows, or true black, brighter colours and stronger contrasts on an OLED model. For example, if you use your TV primarily during the day in a light-flooded living room, you are usually better off with an LCD model. If, on the other hand, you use your TV mainly for movie and series nights, OLED technology is the right choice.
The prejudice of burn-in
OLED TVs are still fighting the prejudice that they are very fragile and have a shorter life than their LCD competitors. The organic light-emitting diodes that make up the pixels in OLED technology consist to a certain extent of hydrocarbons. This means that there is always the possibility of burn-in. This means that if very bright image contents are displayed on dark ones over a longer period of time, an imprint may remain permanently on the display.
Do not confuse: burn-in and memory effect
The burn-in effect occurs when the luminescent materials wear out, causing the brightness of the pixels to decrease. The OLEDs, worn out by very bright image content, darken. The negative of the burnt-in image remains visible on the screen.
The so-called memory effect is also caused by prolonged playback of a very bright image section on a dark background. However, it is not caused by wear and tear of the illuminants, but mainly by the fact that pixel zones heat up and thus react differently to the same control. While a burnt-in image can only be remedied with a great deal of technical effort, with the memory effect it is sufficient to let the display cool down for a while.
In the early days of OLED technology, the risk of burn-in was actually quite high. In the meantime, manufacturers have optimised the materials and built additional electronic aids into their TVs. As a result, the risk of a picture burning into the OLED display is very low under normal circumstances. As a rule, the burn-in effect can only occur if the screen displays a still image for several hours. Manufacturers have also made considerable improvements in terms of lifespan in recent years. About five years ago, for example, the manufacturer LG gave a lifespan of 36,000 hours for its first OLED TVs. For the current models, LG promises 100,000 hours, almost three times the lifespan. This puts OLED models on a par with good LCD sets.
Power consumption and purchase costs
In terms of power consumption, it is difficult to compare TVs with different technologies. With LCD models, power consumption depends very much on how bright the backlight is set. With OLEDs, on the other hand, the content of the picture determines how much power the TV needs. For bright picture content, more power is needed; for the display of black, the corresponding light-emitting diodes do not consume any power at all because they are simply off. In the race for the lowest power consumption, we can therefore only report a draw between LCD and OLED.
Many consumers see the still comparatively high price as the biggest disadvantage of OLED models compared to LCD sets. For example, they have to budget at least 1,500 euros for an OLED TV, while LCD models in the same size are already available from under 1,000 euros.
QLED as a competitor to OLED?
If you are looking for a new TV, you might stumble across the term QLED. Strictly speaking, this is not a new technology for picture reproduction, but rather a further development of LCD from Samsung. The manufacturer uses quantum dot nanocrystals for its QLED models. These special liquid crystals enable a similarly high picture quality as OLED TV sets with higher brightness. However, the QLED models do not quite match OLED TVs in terms of black and contrast. Only time will tell whether Samsung will succeed in ousting OLED technology from the market.

In summary: OLED, QLED or LCD?
For readers who are still unsure which technology is right for their needs, the following table offers some guidance. In it, we compare OLED and LCD TVs and, for the sake of completeness, the special QLED models once again in terms of their most important features. If a technology performs “very well” in a comparison, it receives five stars in our table; for an “unsatisfactory” it receives zero stars.
| Eigenschaft | OLED | QLED | LCD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Representation of black | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Brightness | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Contrast rendition | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Colour rendering | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Even illumination | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Sharpness of movement | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Picture quality in bright surroundings | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Picture quality in dark surroundings | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Picture quality when viewed from the side | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Flat screen | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Model selection | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Lifetime | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Energy efficiency | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Price | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ |
The screen
If you have decided on a technology before buying your new TV, you have of course not yet reached the end of your purchase decision. Depending on the manufacturer and model, OLED TVs differ in terms of various properties and features. The most important features concern the screen. They include size, resolution and shape (flat or curved model).
Resolution and picture quality
The resolution of a TV tells you how many pixels make up the picture. The higher the resolution, the sharper and more detailed the picture. You don’t really have to make a decision about the resolution of your new OLED TV, because all current models offer a high Ultra HD resolution of 3,840 x 2,160 pixels (also known as 4K). To make sure you also get the most out of the high resolution, the content you want to watch on the TV should have the same high resolution.
Soon even sharper pictures in 8K
Ultra-HD is not the end of the line. Already at the IFA 2018 technology fair, the next generation of TVs with even higher resolution was presented: 8K TVs with 7,680 x 4,320 pixels. Each horizontal line has 8,000 pixels rounded up in their case. Individual pixels are barely visible to the human eye, even at close range. At the moment, 8K televisions still lack the content in 8K quality to take off. It may still take a few years until this is available. Until then, however, 4K TVs with the appropriate source material already offer very good picture quality.
Features to improve picture quality
Although 4K resolution was introduced in 2013, not all films, series and video games are yet available in this quality. To ensure that owners of a 4K TV can still enjoy all content in high picture quality, manufacturers have equipped their TVs with additional features to improve the quality of the content:
Upscaling
Upscaling makes it possible to upscale images with lower pixel density to a higher resolution. For example, you can enjoy HD films in 4K resolution. Upscaling ensures that the stretched image does not become pixelated, as the upscaler calculates similar ones from individual pixels and fills the resulting gaps with them.
HDR
HDR stands for “High Dynamic Range” and refers to a technology that improves the contrast range and colour brilliance and enables sharply detailed images. Both the film material and the TV set must support HDR technology. Televisions that support HDR are marked with the label “Ultra HD Premium”.
Screen size
Basically, OLED TVs are something for fans of large images in high quality. Surprisingly, the TVs are not available in smaller formats at all. Currently, they are only available in the following three sizes:
- 55 inches (around 140 centimetres screen diagonal)
- 65 inches (around 165 centimetres screen diagonal)
- 77 inches (around 196 centimetres screen diagonal)

Which size is the right one for OLED TVs with 4K resolution does not necessarily depend on the size of the room, but is more a question of taste and cost. The rules of thumb regarding the distance between the seat and the screen, such as minimum seat distance = 2 x screen diagonal, are invalid for images in 4K. Because of the high resolution and picture quality, the individual pixels are not recognisable even at close range, so that the picture appears clear, sharp and detailed. A seating distance of just under a metre is completely sufficient with a good OLED TV and appropriate source material.
Nevertheless, the fundamental question of space is not entirely moot. After all, the screen must have enough space in the room. And whether it is really fun to watch a screen with a diameter of almost two metres from only one metre away is the other question.
Flat or curved?
Like LCD TVs, OLED models are not only available in flat versions, but also as curved TVs. The curved version has some advantages, especially with large screens, and supports the strengths of OLED technology. Due to the curved surface, the viewing angle on the edge areas is less steep, which improves the perception of contrasts. In addition, the curved screen reduces optical distortions. A prerequisite for this, however, is that the viewer sits centrally in front of his TV set. If the viewing angle is more oblique, the picture quality decreases. In addition, reflections are more present on a curved TV than on a flat-screen model. So flat-screen TVs are more suitable for rooms flooded with light and film evenings with several people.

Special lighting systems
Some manufacturers equip their OLED TVs with special lighting systems. The best known so far is Ambilight from Philips. TVs with Ambilight have lights on the sides of the set. These constantly adjust their colour to the currently dominant colour of the TV picture and illuminate the surroundings as well. With Ambilight Surround, the top of the TV is also equipped with lights.
Ambilight ensures that the viewer perceives the TV picture as larger. Because the TV picture is no longer the only source of light, Ambilight is also easier on the eyes. If you want to benefit from the advantages of Ambilight, you no longer have to use a Philips set. Various manufacturers offer sets for retrofitting Ambilight to any TV system.
Features
After choosing the technology and the right screen, the third step in the selection process is to decide which features and additional functions the OLED TV should have.
Use smart features
Almost all new TV models are now so-called smart TVs. These are characterised by the possibility of installing apps that provide practical additional functions. To use them, the smart TVs need an internet connection. Therefore, smart TVs are equipped with interfaces for LAN or WLAN. In most cases, a WLAN card is built in directly, otherwise you use a WLAN stick.

Users download the desired apps from a kind of library, similar to a tablet or smartphone. Which apps are available depends on the operating system of your Smart TV. Popular smart TV apps are, for example, those of video-on-demand services such as Netflix or Amazon Prime as well as video and music portals such as YouTube or Spotify. But weather apps, browsers or games can also be used on the smart TV. Remote control apps for the smartphone are also practical and increase the ease of use.
Different operating systems of Smart TVs
Which operating system the Smart TV comes with depends on the manufacturer. The most popular smart TV operating systems include:
- Android TV (used by Sony, Philips and Sharp).
- Firefox OS (used by Panasonic)
- Tizen OS (used by Samsung)
- WebOS (used by LG)
- Roku TV (used by Haier, Highsense, TCL and Sharp)
Receiving different signals
The built-in tuners determine which paths the TV can use to receive signals. The standard for modern TVs is now a triple tuner with the following reception options:
- DVB-C (cable TV)
- DVB-S2 (successor standard to DVB-S; satellite television)
- DVB-T2 (successor standard to DVB-T; antenna television)
If you choose an OLED TV with a triple tuner, this means that you can receive cable, satellite and antenna TV with your TV without needing a set-top box.
In the meantime, there are even models with a quattro tuner. With these, the IPTV tuner for Internet TV is added to the three reception paths mentioned.
If the OLED TV has a twin tuner, this means that the available reception paths are each available twice. This has the advantage that users can, for example, record their favourite series on one channel while watching the news on another.
Recording content via USB
The days when we used video recorders and VHS tapes to record television are long gone. Ideally, there is no longer any need for a recording device at all. Many modern televisions have an integrated recording function. To use it, all you have to do is connect a USB medium to the TV. Depending on your personal preference, this can be either a handy USB memory stick or a USB hard drive. The latter is a little more expensive to buy than a stick, but of course it also offers a lot more storage space.
The most important connections
Basically, the more connections a TV has, the better. Particularly important are HDMI connections, which are used for the fully digital transmission of picture and sound in high quality. Users use them to connect external devices such as game consoles, Blu-ray players and home cinema systems to their TV. If you want to connect several devices simultaneously via HDMI, you need several HDMI connections. Most current OLED TVs have at least three HDMI connections, often even four. Also important are several USB ports for recording as well as playing media files; two or three are common.
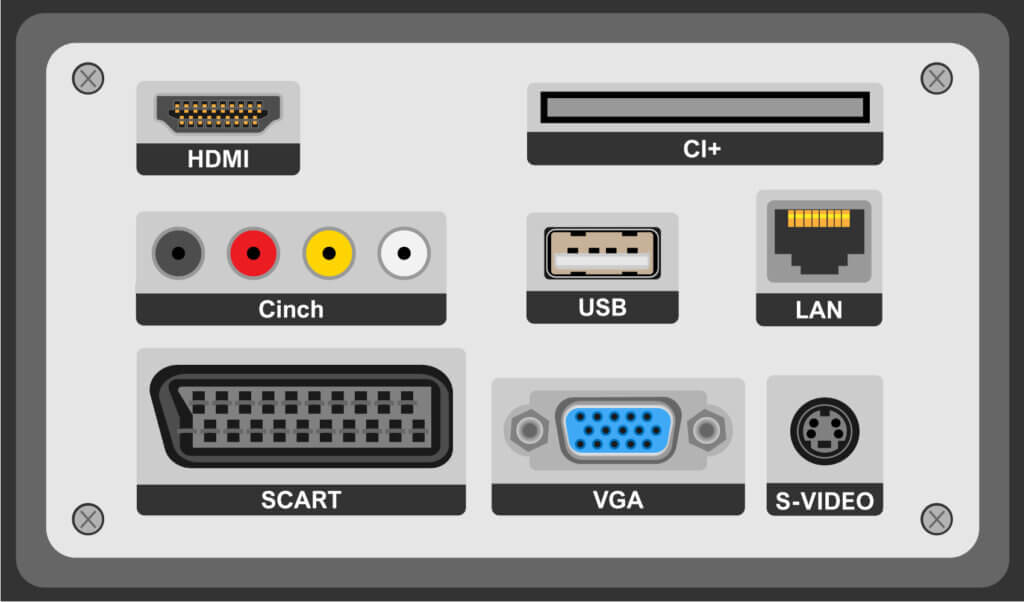
Since all OLED TVs are usually smart TVs, the internet connection is actually a matter of course. Most models come with both a LAN connection (wired) and a WLAN module (wireless).
If you want to receive private pay channels, you must also make sure that a CI+ slot (Common Interface) is available. A special HD+ card is then inserted into this slot, via which the channels are activated for a certain monthly amount.
If you want to connect older devices to your television, you will also need the following connections:
- SCART: to transmit analogue audio and video signals (the “old HDMI”, so to speak).
- S-Video input: for connecting old camcorders
- VGA: to connect older computers without HDMI interface
- Cinch outputs: for connecting older audio systems or AV receivers
- Optical digital output: modern RCA replacement
OLED TV manufacturers
Various manufacturers are constantly wooing consumers with new features and improvements to their OLED TVs. For a better overview, we present the most popular OLED TV manufacturers with their model series and their special features below.
LG – the OLED pioneers
The Korean brand LG Electronics was founded more than 60 years ago and brought the first Korean TV set onto the market eight years later. In 2009, the manufacturer was allowed to call itself the second largest LCD TV brand in the world. And LG is also considered a pioneer in OLED TVs: in 2013, the Korean company brought the first 55-inch OLED TV onto the market.
With LG Signature, the manufacturer has now founded its own premium label, in which it says it combines impressive design with the latest technology. Of course, OLED TVs should not be missing here: Currently, there are three different models of LG Signature in the sizes 65 and 77 inches. The premium models cost between 3,000 and 12,000 euros. They feature particularly thin displays (wallpaper), an innovative processor (a9) and powerful moving surround sound (Dolby Atmos).
But consumers looking for cheaper OLED TVs will also find what they are looking for at LG. Starting at 1,200 euros, 55-inch TVs are available here. Overall, LG still offers the largest model selection among OLED TV manufacturers. LG is the only manufacturer that currently has curved TVs with OLED technology in its range. In addition, LG OLED models perform best in Stiftung Warentest tests.
| Model series | LG Signature W8, LG Signature G8, E8, C8, B8 |
| Screen sizes | 55 inch, 65 inch, 77 inch |
| Lowest price | 1,200 euros |
| Highest price | 12,000 euros |
| Special features | Large model selection, wallpaper TVs, optimised processor, powerful surround sound, very good test results |
Panasonic – Hollywood for the home
Only four years after LG Electronics launched the first OLED TV, the electronics company Panasonic also jumped on the OLED bandwagon. In the meantime, Panasonic has the picture-strong TV sets in all three usual sizes in its range. Depending on the model, they cost between 1,900 and 10,000 euros. A special feature: Panasonic offers a professional calibration service for its OLED TVs to optimise the picture quality.
The manufacturer advertises its OLED TVs with the slogan “Experience Hollywood at home”. Specialists from Hollywood have optimised the current model series. A newly developed HCX processor is supposed to enable outstanding picture quality. In the Stiftung Warentest test, Panasonic’s OLED models scored “good”. Panasonic even shares first place with LG in the 55-inch TV category.
| Model series | GZW, EZW, FZW |
| Screen sizes | 55 inch, 65 inch, 77 inch |
| Lowest price | 1,900 euros |
| Highest price | 10,000 euros |
| Special features | Large model selection, good test results, HCX processor, professional calibration service |
Sony – especially flat models
The Japanese electronics company Sony still concentrates primarily on LED TVs, but now also has OLED models in its range. Sony’s OLED models stand out from the competition because they are particularly flat and have very thin frames. This means they can be hung very close to the wall and fit perfectly into the room, similar to a picture frame. Sony’s slimmest OLED model to date is only an impressive 0.3 millimetres deep. Sony’s OLEDTVs run under the BRAVIA model series, which stands for “Best Resolution Audio Visual Integrated Architecture”. With the current models, the manufacturer relies on the Picture Processor X1 Ultimate and thus promises the highest picture quality with rich blacks and natural colours.
Sony’s range includes OLED TVs in the usual three sizes. Depending on the model and size, buyers pay between 2,500 and 13,000 euros.
A Sony speciality: the sound features such as the TV centre speaker mode, where the sound comes from the centre of the screen. Vibration behind the screen creates acoustics that are in harmony with the picture. Acoustic Surface Audio technology ensures that the sound comes directly from the screen.
| Model series | A1, AG8, AF8, AG9, AF9 |
| Screen sizes | 55 inch, 65 inch, 77 inch |
| Lowest price | 2,500 euros |
| Highest price | 13,000 euros |
| Special features | Acoustic Surface Audio, TV-Center-speaker mode, Picture Processor X1 Ultimate, very flat screens |
Loewe – configurable designs for a little more money
With Loewe Technologies, one of the most popular OLED manufacturers is also a German company. Since 2017, the Loewe range has also included OLED TVs, which the manufacturer produces in cooperation with OLED pioneer LG Electronics.
At Loewe, the model series of the TVs are called bild, the speakers klang. OLED TVs are currently available in the bild 3, bild 5 and bild 7 series. A special feature of Loewe: customers can configure the design of their chosen model and thus individually adapt it to their wishes. Among other things, they choose one of the three sizes (55, 65 or 77 inches), the set-up solution (table stand, tilting wall mount or fixed wall mount) and the colour. With the customisable design, Loewe promises that its televisions will fit both in a winding old flat and in a light-flooded, spacious loft. In addition, the bild models are available in sets with the matching klang soundbar.
The current models cost between 2,400 and 16,000 euros, depending on size. This makes them among the higher-priced OLED TVs.
| Model series | Bild3, bild5, bild7 |
| Screen sizes | 55 inch, 65 inch, 77 inch |
| Lowest price | 2,400 euros |
| Highest price | 16,000 euros |
| Special features | Customisable designs, available in sets with speakers, rather high-priced |
Philips – low prices and Ambilight
The technology giant Philips launched the OLED 9 series at the beginning of this year and promises perfect picture quality with the revised P5 engine for image processing. According to the advertising promise, the sound, which engineers from the speaker manufacturer Bowers & Wilkins have developed, is also supposed to be perfect.
A special feature from Philips is the Ambilight technology. The Ambilight models are equipped with additional LEDs that project the colours of the screen onto the walls in real time so that the screen appears larger. Ambilight is also supposed to be easy on the eyes.
Philips currently offers 55- and 65-inch TVs with OLED technology. These cost between 1,500 and 2,800 euros, which is comparatively cheap. However, 77-inch models are still missing from the range.
| Model series | OLED 8, OLED 9 |
| Screen sizes | 55 inch, 65 inch |
| Lowest price | 1,500 euros |
| Highest price | 2,800 euros |
| Special features | Customisable designs, available in sets with speakers, rather high-priced |
Samsung – the opponent
Until now, Samsung was considered a big opponent of OLED TVs. The Korean company relied on its own QLED technology, which offers a similarly high picture quality as OLED, at a slightly lower price. However, Samsung apparently cannot entirely keep its hands off OLED technology. At the beginning of the year, the manufacturer announced that it is currently working on OLED TVs in combination with quantum dots. Samsung promises even richer colours than with previous OLED TVs.









 no reviews
no reviews




